Uma introdução ao algoritmo de classificação de mesclagem
A classificação de mesclagem é um algoritmo de classificação baseado na técnica "dividir para conquistar". É um dos algoritmos de classificação mais eficientes.
Neste artigo, você aprenderá sobre o funcionamento do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem, o algoritmo da classificação por mesclagem, sua complexidade de tempo e espaço e sua implementação em várias linguagens de programação como C ++, Python e JavaScript.
Como funciona o algoritmo de classificação de mesclagem?
A classificação de mesclagem funciona com o princípio de dividir e conquistar. A classificação por mesclagem divide repetidamente uma matriz em duas submatrizes iguais até que cada submatriz consista em um único elemento. Finalmente, todas essas submatrizes são mescladas de forma que a matriz resultante seja classificada.
Este conceito pode ser explicado de forma mais eficiente com a ajuda de um exemplo. Considere uma matriz não classificada com os seguintes elementos: {16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18}.
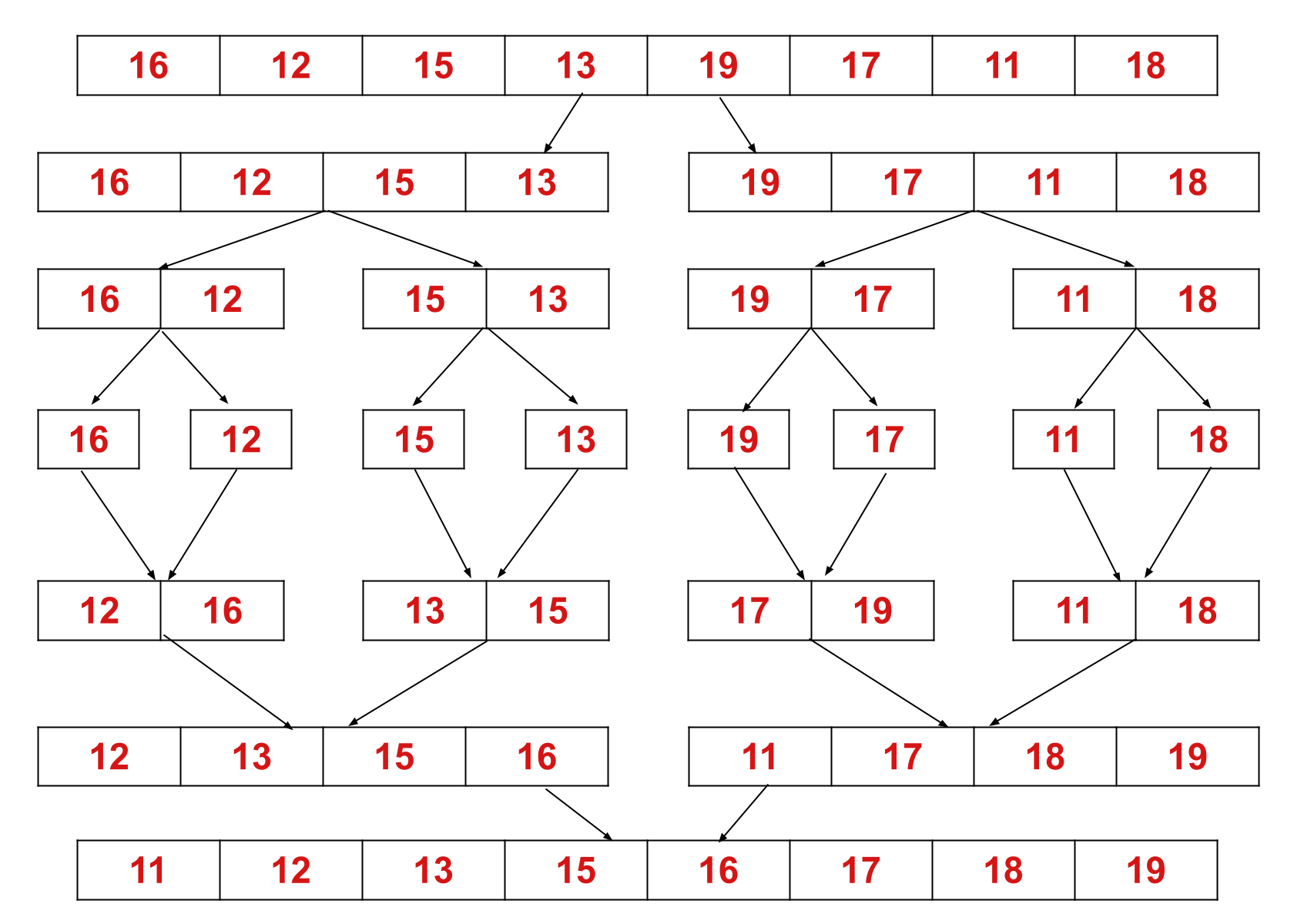
Aqui, o algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem divide a matriz em duas metades, chama a si mesmo para as duas metades e, em seguida, mescla as duas metades classificadas.
Algoritmo de mesclagem de classificação
Abaixo está o algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem:
MergeSort(arr[], leftIndex, rightIndex)
if leftIndex >= rightIndex
return
else
Find the middle index that divides the array into two halves:
middleIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex-leftIndex)/2
Call mergeSort() for the first half:
Call mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex)
Call mergeSort() for the second half:
Call mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex)
Merge the two halves sorted in step 2 and 3:
Call merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex)
Complexidade de tempo e espaço do algoritmo de classificação de mesclagem
O algoritmo de classificação Merge pode ser expresso na forma da seguinte relação de recorrência:
T (n) = 2T (n / 2) + O (n)
Depois de resolver essa relação de recorrência usando o teorema do mestre ou o método da árvore de recorrência, você obterá a solução como O (n logn). Assim, a complexidade de tempo do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem é O (n logn) .
O melhor caso de complexidade de tempo da classificação de mesclagem: O (n logn)
A complexidade de tempo médio de caso da classificação de mesclagem: O (n logn)
O pior caso de complexidade de tempo da classificação de mesclagem: O (n logn)
A complexidade do espaço auxiliar do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem é O (n), pois n espaço auxiliar é necessário na implementação da classificação por mesclagem.
Implementação C ++ do Algoritmo de Classificação de Mesclagem
Abaixo está a implementação C ++ do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem:
// C++ implementation of the
// merge sort algorithm
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// This function merges two subarrays of arr[]
// Left subarray: arr[leftIndex..middleIndex]
// Right subarray: arr[middleIndex+1..rightIndex]
void merge(int arr[], int leftIndex, int middleIndex, int rightIndex)
{
int leftSubarraySize = middleIndex - leftIndex + 1;
int rightSubarraySize = rightIndex - middleIndex;
// Create temporary arrays
int L[leftSubarraySize], R[rightSubarraySize];
// Copying data to temporary arrays L[] and R[]
for (int i = 0; i < leftSubarraySize; i++)
L[i] = arr[leftIndex + i];
for (int j = 0; j < rightSubarraySize; j++)
R[j] = arr[middleIndex + 1 + j];
// Merge the temporary arrays back into arr[leftIndex..rightIndex]
// Initial index of Left subarray
int i = 0;
// Initial index of Right subarray
int j = 0;
// Initial index of merged subarray
int k = leftIndex;
while (i < leftSubarraySize && j < rightSubarraySize)
{
if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in L[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (i < leftSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in R[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (j < rightSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
void mergeSort(int arr[], int leftIndex, int rightIndex)
{
if(leftIndex >= rightIndex)
{
return;
}
int middleIndex = leftIndex + (rightIndex - leftIndex)/2;
mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex);
mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex);
merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex);
}
// Function to print the elements
// of the array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
cout << "Unsorted array:" << endl;
printArray(arr, size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, size - 1);
cout << "Sorted array:" << endl;
printArray(arr, size);
return 0;
}Resultado:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19Implementação de JavaScript do algoritmo Merge Sort
Abaixo está a implementação JavaScript do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem:
// JavaScript implementation of the
// merge sort algorithm
// This function merges two subarrays of arr[]
// Left subarray: arr[leftIndex..middleIndex]
// Right subarray: arr[middleIndex+1..rightIndex]
function merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex) {
let leftSubarraySize = middleIndex - leftIndex + 1;
let rightSubarraySize = rightIndex - middleIndex;
// Create temporary arrays
var L = new Array(leftSubarraySize);
var R = new Array(rightSubarraySize);
// Copying data to temporary arrays L[] and R[]
for(let i = 0; i<leftSubarraySize; i++) {
L[i] = arr[leftIndex + i];
}
for (let j = 0; j<rightSubarraySize; j++) {
R[j] = arr[middleIndex + 1 + j];
}
// Merge the temporary arrays back into arr[leftIndex..rightIndex]
// Initial index of Left subarray
var i = 0;
// Initial index of Right subarray
var j = 0;
// Initial index of merged subarray
var k = leftIndex;
while (i < leftSubarraySize && j < rightSubarraySize)
{
if (L[i] <= R[j])
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
}
else
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in L[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (i < leftSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
// If there're some remaining elements in R[]
// Copy to arr[]
while (j < rightSubarraySize)
{
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
function mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, rightIndex) {
if(leftIndex >= rightIndex) {
return
}
var middleIndex = leftIndex + parseInt((rightIndex - leftIndex)/2);
mergeSort(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex);
mergeSort(arr, middleIndex+1, rightIndex);
merge(arr, leftIndex, middleIndex, rightIndex);
}
// Function to print the elements
// of the array
function printArray(arr, size) {
for(let i = 0; i<size; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
document.write("<br>");
}
// Driver code:
var arr = [ 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 ];
var size = arr.length;
document.write("Unsorted array:<br>");
printArray(arr, size);
mergeSort(arr, 0, size - 1);
document.write("Sorted array:<br>");
printArray(arr, size);Resultado:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19
Implementação Python do algoritmo Merge Sort
Abaixo está a implementação Python do algoritmo de classificação por mesclagem:
# Python implementation of the
# merge sort algorithm
def mergeSort(arr):
if len(arr) > 1:
# Finding the middle index of the array
middleIndex = len(arr)//2
# Left half of the array
L = arr[:middleIndex]
# Right half of the array
R = arr[middleIndex:]
# Sorting the first half of the array
mergeSort(L)
# Sorting the second half of the array
mergeSort(R)
# Initial index of Left subarray
i = 0
# Initial index of Right subarray
j = 0
# Initial index of merged subarray
k = 0
# Copy data to temp arrays L[] and R[]
while i < len(L) and j < len(R):
if L[i] < R[j]:
arr[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
else:
arr[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
k = k + 1
# Checking if there're some remaining elements
while i < len(L):
arr[k] = L[i]
i = i + 1
k = k + 1
while j < len(R):
arr[k] = R[j]
j = j + 1
k = k + 1
# Function to print the elements
# of the array
def printArray(arr, size):
for i in range(size):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
print()
# Driver code
arr = [ 16, 12, 15, 13, 19, 17, 11, 18 ]
size = len(arr)
print("Unsorted array:")
printArray(arr, size)
mergeSort(arr)
print("Sorted array:")
printArray(arr, size)
Resultado:
Unsorted array:
16 12 15 13 19 17 11 18
Sorted array:
11 12 13 15 16 17 18 19Compreender outros algoritmos de classificação
A classificação é um dos algoritmos mais usados na programação. Você pode classificar os elementos em diferentes linguagens de programação usando vários algoritmos de classificação, como classificação rápida, classificação por bolha, classificação por mesclagem, classificação por inserção, etc.
A classificação por bolha é a melhor escolha se você deseja aprender sobre o algoritmo de classificação mais simples.

